Cervical papilloma is one of the most common human papillomavirus infections. Skin refers to the formation of skin.
Causes of neck papillomas
There is an etiological reason why papillomas begin to grow in the human body or in other areas - infection with human papillomavirus (HPV), a member of the papovavirida family. There are more than 100 serotypes of this pathogenic agent, each of which is responsible for the appearance of other clinical manifestations of the disease (papilloma, condyloma, warts - these concepts are synonymous, different names are associated with localization features in a particular area).
The main routes of infection are household and genital warts (perianal condyloma). The virus can only enter the skin in the presence of micro-injuries or open wounds, otherwise it cannot pass through the skin's protective barrier.
Pathogenic information
- Regardless of gender (more common in women than men), age or region (according to some sources, 2/3 of the planet is infected with this virus).
- It contains double-stranded, twisted ring DNA that is able to integrate into the human genome.
- Infection of some strains is associated with a carcinogenic risk, especially in the case of permanent injury. Cervical papillomas are caused by non-oncogenic strains of the virus.
- The virus goes through two main stages in the process of division. In the first stage, it is in an episomic (free) form, while the main division of the viral particle occurs. This phase is reversible (long-term remission occurs after treatment). Second, at the integrative stage, the virus is implanted in the cell's genome (the first step in cell destruction and malignancy). The first stage is temporary and relatively quick, while the second explains the presence of hidden and carriers.
- The basal layer of the epidermis is affected by the virus. In the remaining layers, the pathogen can be stored, but not separated. If the virus is present in the genital layer, as it grows, the normal differentiation of cells in all layers of this region is disrupted, especially at the level of the thorny layer.
- There is a tendency for long-term asymptomatic transport in the body (from several months to a year). It is very rare to detect a specific case of infection - for this reason, treatment is started at the time of strong clinical manifestations, not at the first vague symptoms.
- Bivalent and quadrivalent vaccines, which are particularly effective against the 16 and 18 most oncogenic strains, are used to prevent infection.
predetermining factors
- Lack of hygiene. Since the virus can remain active in the environment for a long time, it is necessary to carefully follow the rules of personal hygiene when visiting public places (swimming pool, bath, gym).
- Injuries to the skin. Microcracks or nails on the skin (such as rubbing the collar of a shirt or neck) are enough for the virus to enter.
- Impaired immune system function. With immune deficiencies of various genesis, favorable conditions are created for the development of various infections. For example, frequent colds and infections can weaken the immune system and cause skin papillomas.
- Self-infection by scratching the skin.
- Systemic disorders of life (stress, lack of physical activity, malnutrition). These factors affect the functioning of all metabolic processes in the body and lead to a decrease in the skin's barrier function.
- Environmental factors influencing the decline of the body's defenses (hypothermia, excessive ultraviolet exposure).
Appearance of the disease
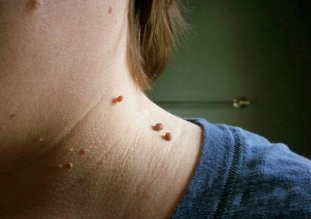
Papillomas of the neck in the picture look like this:
- Growths are usually broad and protrude significantly above the skin surface. The base of the papilloma is represented by a thin leg (in this case, the formation occupies a hanging position). In the second option, the risk of injury is much higher.
- The boundaries of education are uniform and clear.
- The color is no different from the surrounding skin. In rare cases, it may be a little paler or darker than the surrounding tissue.
- The surface is usually smooth. Sometimes a papilloma can grow on the upper side, which makes its surface ribbed.
- Diameters vary from 1-3 mm to a few centimeters (small papillomas are more common).
- Location anywhere on the neck (back, side). At times, they even look confused.
As a rule, there are many sores located along the folds of the skin.
In very rare cases, papillomas in the neck can be malignant, ie they can turn into skin tumors. It can occur as a result of infection with the oncogenic HPV strain.
Signs of a harmful transformation are as follows:
- color change and heterogeneity (polymorphism);
- border change (blurring, loss of definition);
- appearance of asymmetry (when drawing a line through the conventional center of the formation, it is impossible to get two identical halves);
- intensive growth;
- bleeding or ulcer (a non-specific symptom because it is characteristic of a newly formed injury);
- itching, burning, itching;
- dropouts appear (little girls form around the center).
The appearance of these symptoms does not necessarily mean that the papilloma is malignant, but it does mean that you should see a doctor and make a differential diagnosis, knowing that you are talking about a common inflamed mole or skin cancer.
How to get rid of neck papillomas
Treatment of cervical papillomas is carried out only in a complex way, simultaneously affecting the pathological focus on the skin and the pathogen in the blood.
There are several ways to fight:
method |
Description |
medicines |
The use of cytostatics, immunomodulators is designed to suppress the growth of the viral agent in the affected area and reduce its concentration in the blood. Some drugs (keratolytics) are used directly to destroy skin growth (cauterizing and causing tissue necrosis). |
Physical Methods |
Cryodestruction, laser therapy, electrocoagulation. They aim to get rid of papillomas in the neck and other parts of the body. These techniques allow you to restore the aesthetic appearance of exposed areas and remove the viral reservoir - the skin neoplasms themselves, but they do not completely eliminate the virus from the body. |
combination therapy |
Combines the two previous options, so it's the most efficient. |
Treating papillomas at home with folk remedies (such as celandine juice) is ineffective and often dangerous, but in any case, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Physical methods of destruction
The following physical methods can be used to effectively reduce formation:
method |
Description |
Local effects with concentrated acid solutions |
A 1. 5% solution of zinc chloropionate in 50% 2-chloropropionic acid, nitric, acetic, oxalic, lactic acids and copper nitrate trihydrate, etc. were used. The procedure is performed in an outpatient setting by a specialist (dermatovenereologist, cosmetologist) in accordance with surgical rules. . . . The agent is formed with the help of a layer and applied until the color of the formation becomes clear (as soon as this occurs, use should be stopped immediately). On average, 1-2 treatments are needed to completely cure papilloma. |
Electrocoagulation |
With the help of a special electric knife, point cutting of structures is performed without affecting the underlying tissues (minimal effect on healthy skin cells). The method is most convenient when the shape has a long stem and small size. |
Cryodestruction |
Under the influence of liquid nitrogen, very low temperatures lead to tissue necrosis. It is better to clean this way of education on a broad basis. The duration of exposure to nitrogen is chosen by a specialist (1-5 minutes). Burns occur after moxibustion and heal in an average of 10 days. |
Laser destruction |
The most modern and gentle way to stop growth in prominent places like the neck. Has the most positive reviews. Adjust the focus of the app from 5 seconds to 3 thousand lights in continuous mode. The duration of treatment is much shorter than other methods (5-7 days). The technique is associated with minimal trauma to the surrounding tissues due to the high accuracy of operations. |
Classical surgical removal (scalpel excision) |
Very rare, with a major injury or suspected malignancy. This is because the sores are often large, scattered around the neck, and too small for excision, and scarring may remain after surgery, creating a cosmetic defect. |














































































